get_D() and get_y() in Curve StableSwap
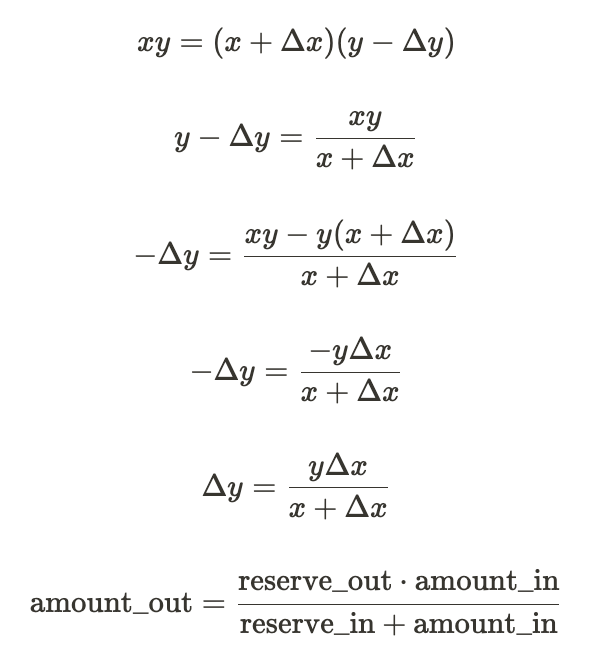
get_D() and get_y() in Curve StableSwap This article shows algebraically step-by-step how the code for get_D() and get_y() are derived from the StableSwap invariant. Given the StableSwap Invariant: $$ An^n\sum x_i +D=An^nD+\frac{D^{n+1}}{n^n\prod x_i} $$ There are two frequent math operations we wish to conduct with it: Compute $D$ given fixed values for $A$, and the […]